If you perform a quick Google search for "What is the most useful math for business?", the answer is almost always Optimization.
Optimization is the science of finding the "Best" possible outcome—whether that means finding the Maximum Profit, Minimum Cost, or Maximum Structural Strength. This is where Calculus pays the bills.
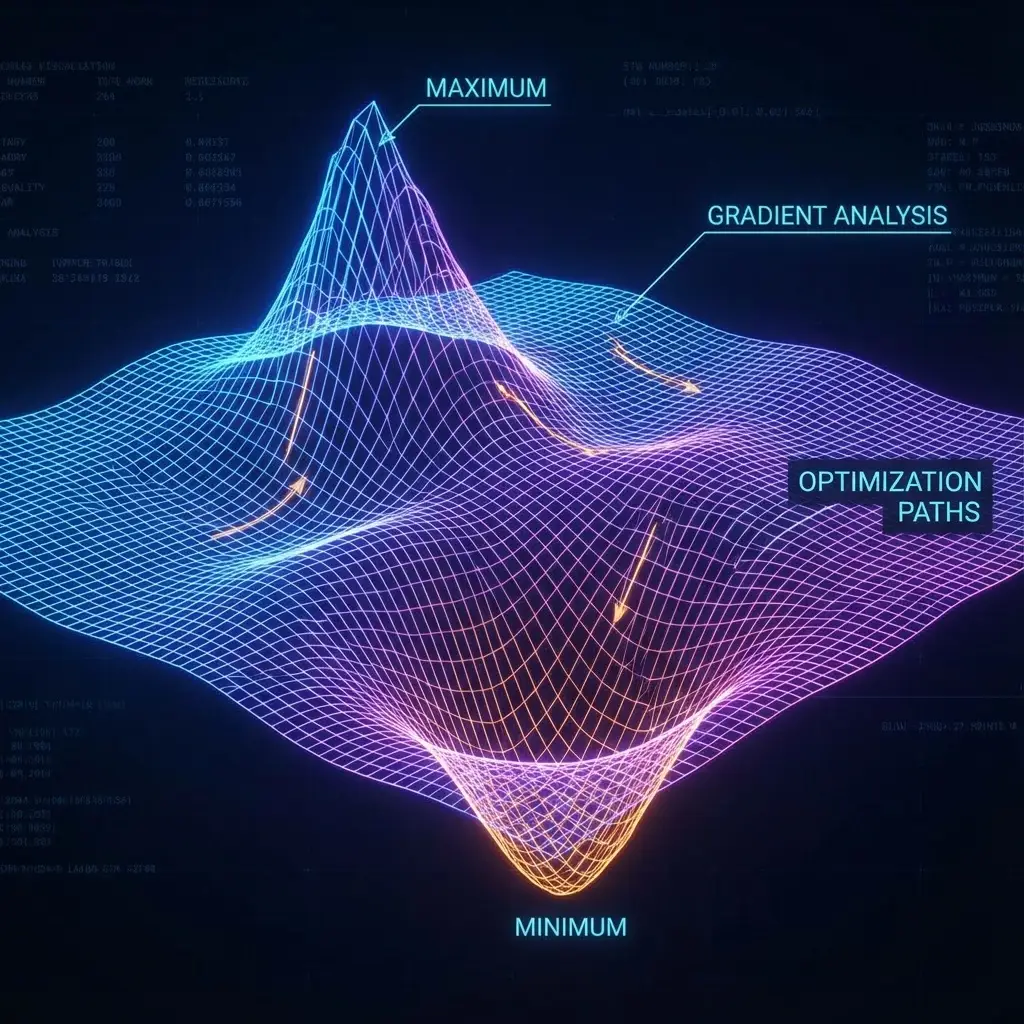
1. The Logic of Peaks and Valleys
Imagine a roller coaster track. At the very highest peak (Maximum), for a split second, the car is completely flat. It's not going up, and it's not going down. The slope is Zero.
The same is true for the lowest valley (Minimum).
This gives us the Golden Rule of Optimization: To find the Max or Min, take the derivative and set it to zero.
2. Step-by-Step Optimization Strategy
Step 1: The Constraint Equation
Real life has limits. You only have $500 budget. You only have 100 meters of fencing. Write an equation for what you are limited by.
Step 2: The Objective Equation
Write an equation for what you want to optimize (e.g., Area = x * y).
Step 3: Combine and Differentiate
Use the Constraint to solve for one variable, plug it into the Objective, take the derivative, set to 0, and solve.
3. Classic Example: The Farmer's Fence
A farmer has 100m of fence and wants to enclose the biggest possible rectangular area against a river (so he only needs 3 sides).
Sides: x, x, and y. Length = 2x + y = 100.
Area = x * y.
Substitute y: y = 100 - 2x.
Area(x) = x * (100 - 2x) = 100x - 2x².
Derivative A'(x) = 100 - 4x.
Set to 0: 100 = 4x -> x = 25.
If x=25, y=50. Area = 1250m².
If he had used a square (25x25x25) or long thin strip, the area would be smaller. Calculus found the perfect shape instantly.
4. The Second Derivative Test
Wait, if Slope=0 at both the Peak and the Valley, how do we know if we found a Max (Good) or a Min (Bad)?
We check the Concavity (Second Derivative).
- f''(x) > 0 (Positive): The graph is smiling (cup shape). It's a Minimum.
- f''(x) < 0 (Negative): The graph is frowning. It's a Maximum.
5. Real World Applications
- Logistics: FedEx uses optimization algorithms to find the shortest route to deliver 1,000 packages.
- AI Training: Neural networks "optimize" their accuracy by minimizing the "Loss Function" (Gradient Descent).
- Finance: Portfolio managers optimize the ratio of Risk vs Reward.
6. FAQ
Q: What if the derivative is never zero?
A: Then the maximum is at the endpoint of your interval (e.g., if you want to maximize profit and profit just goes up forever, the max is at "Infinity" or whatever your maximum production capacity is).
Q: Can I optimize with more than 2 variables?
A: Yes, but you need Multivariable Calculus (Lagrange Multipliers). The concept is the same: gradients must align.
Conclusion
Optimization turns "guessing" into "knowing". Instead of hoping you made the right business decision, you can prove mathematically that no other decision could possibly yield a better result.